Introduction:
In the dynamic landscape of software development, ensuring the seamless functioning of Learning Management Systems (LLMS) in production is paramount. LLM testing, or Learning Management System testing, is a critical phase that demands meticulous attention to detail. In this article, we will delve into the strategies and best practices for testing LLMS in production environments, shedding light on key aspects to guarantee a robust and error-free user experience.
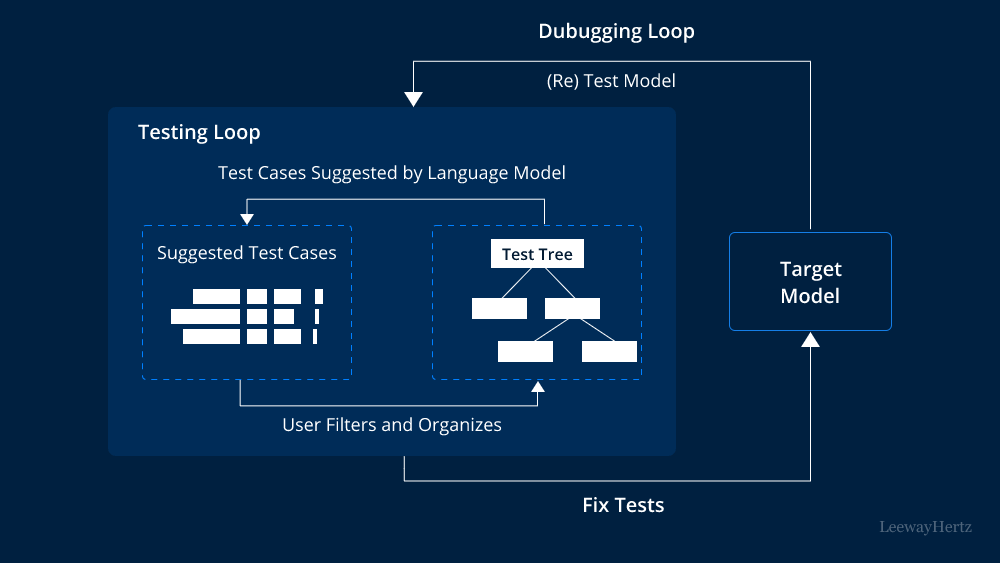
Understanding the Importance of LLM Testing:
Learning Management Systems serve as the backbone for educational platforms, delivering content, managing users, and tracking progress. Testing in a production environment is crucial to identify and rectify potential issues before they impact end-users. A flawless LLM ensures a positive learning experience, fostering user engagement and satisfaction.
1. Test Environments and Data Preparation:
Before delving into production testing, it is essential to set up realistic test environments that mirror the production environment closely. This includes identical hardware configurations, network settings, and databases. Additionally, prepare realistic test data to simulate actual usage scenarios, ensuring that the LLM undergoes thorough testing under conditions it will encounter in the live environment.
2. Regression Testing:
Implementing changes or updates to an LLM can introduce unforeseen issues. Regression testing is a crucial step to ensure that new features or modifications do not negatively impact existing functionalities. Automated testing tools can streamline this process, allowing for the swift and comprehensive validation of the entire system after changes have been implemented.
3. Performance Testing:
LLMS often face heavy loads during peak usage times. Performance testing helps gauge the system’s ability to handle concurrent users, ensuring it can deliver content efficiently without compromising speed or reliability. Load testing, stress testing, and scalability testing are integral components of performance testing, allowing developers to identify and address potential bottlenecks.
4. Security Testing:
As educational platforms deal with sensitive user data, security testing is non-negotiable. Conduct thorough security assessments to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses. This includes testing user authentication, data encryption, and protection against common security threats such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting. A secure LLM not only protects user data but also builds trust among users and stakeholders.
5. User Acceptance Testing (UAT):
User acceptance testing involves validating the LLM’s functionality from the end user’s perspective. This step ensures that the system aligns with user expectations and requirements. Engaging real users in the testing process provides valuable feedback on the system’s usability, accessibility, and overall user experience.
6. Monitoring and Logging:
Implement robust monitoring and logging mechanisms within the production environment. Continuous monitoring helps detect issues in real-time, allowing for proactive intervention. Comprehensive logging facilitates post-incident analysis, aiding in the identification of root causes and the development of preventive measures.
Conclusion:
Testing LLMs in a production environment is a multifaceted process that demands a strategic and comprehensive approach. From setting up realistic test environments to conducting thorough security assessments, each step plays a crucial role in ensuring the reliability and functionality of Learning Management Systems. By incorporating these best practices into your LLM testing strategy, you can navigate the complexities of production testing with confidence, ultimately delivering a seamless and enriching learning experience for end-users.